
What is a Mobile AI Gateway?
A mobile AI gateway is a security and routing layer that sits between your mobile app and AI providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, or Gemini. Instead of calling those APIs directly from the app (and shipping API keys in your binary), the gateway issues short-lived, device-aware tokens and forwards requests on behalf of the app, applying policies, monitoring usage, and keeping your secrets off the phone. Gate/AI is a mobile-first AI Gateway built specifically for this use case: secure AI access for iOS, Android, and cross-platform apps without running your own backend. 
If you’ve ever been tempted to paste an OpenAI key straight into your app because “it’s just a side project” or “I don’t have time to build a backend,” this is the problem a mobile AI gateway solves.
First: what is an AI Gateway?
Before we get into “mobile AI gateway,” it helps to define the broader term: AI gateway.
An AI gateway is like an API gateway that understands AI workloads. It sits in front of one or more LLM or generative AI providers and handles things like:
- Forwarding requests to different models or providers
- Applying security and access control policies
- Logging, metering, and rate limiting usage
The important bit: clients don’t talk to OpenAI, Anthropic, or others directly. They talk to the gateway, and the gateway talks to the providers.
Traditional AI gateways are mostly designed with backend callers in mind: web servers, microservices, data pipelines. Those callers are already in your trusted environment, behind firewalls, with secrets stored in something like AWS KMS or HashiCorp Vault.
Mobile apps are the opposite of that.
Why mobile needs its own AI gateway design
From a security perspective, a mobile app is an untrusted client:
- The binary can be decompiled and inspected.
- The network can be intercepted or replayed.
- The app can run on rooted/emulated devices with hooks everywhere.
If you embed long-lived API keys in your app and point it straight at an AI provider, you are effectively giving an attacker your backend’s identity. Once they have that key, they can:
- Hammer the provider’s API from their own scripts.
- Run up your bill.
- Send abusive or illegal content that’s still tied to your account.
A generic AI gateway doesn’t fix that by itself, because it still expects to be called from a safe environment. It will take your long-lived key or token and secure things from there. But from a mobile app, the problem is before the gateway: you still need to safely authenticate the app and device to the gateway in the first place.
That’s what a mobile AI gateway is built to handle.
What makes a mobile-first AI gateway different?
A mobile-first gateway like Gate/AI is designed around a few hard truths:
- You cannot trust the client. Assume your app will be decompiled, proxied, and run on compromised devices.
- You still want to ship without a custom backend. Many mobile teams don’t want to stand up and maintain an API just to talk to OpenAI.
- You still want real security. “It’s fine, it’s just a test key” stops being fine the moment you ship to production.
To square that circle, a mobile AI gateway does more than a generic AI proxy:
- It never requires you to ship provider secrets in the app. Your OpenAI key (or Anthropic, or Gemini) lives in the gateway, not in the binary.
- It verifies the calling app and device using mechanisms like Apple App Attestation or Android Play Integrity before it trusts a request.
- It issues short-lived, device-bound tokens instead of long-lived API keys. Tokens are scoped and time-boxed so they’re painful to abuse.
- It enforces per-device and per-user policy: rate limits, usage caps, and other guardrails specific to mobile usage patterns.
That combination is what lets you call AI providers directly from the app—no custom backend—without falling into the “just ship the secret” trap. 
How Gate/AI’s mobile AI gateway fits into your app
At a high level, a Gate/AI-powered request looks like this:
flowchart LR
A[Mobile App] -->|attested request| B[Gate/AI Mobile AI Gateway]
B -->|short-lived, device-bound token| C[Gate/AI Policy + Monitoring]
C -->|provider API call| D[(AI Provider\nOpenAI / Anthropic / Gemini)]
D -->|streamed response| B --> A
- Your mobile app talks to Gate/AI, not directly to OpenAI or others.
- Gate/AI checks that the request comes from a real, untampered app on a real device.
- Gate/AI issues or validates a short-lived token, applies policy, and forwards the call to the AI provider.
- Responses stream back through Gate/AI to your app.
You keep your implementation simple—call an HTTPS endpoint from the app—but all the security-critical pieces live on the gateway.
Zero-trust for mobile AI access
When we say Gate/AI is “zero-trust,” we mean two things:
- We don’t trust any device or app by default. Every request has to prove that it’s coming from a genuine app on an acceptable device.
- We don’t trust long-lived secrets in untrusted environments. Nothing in your shipping binary should grant unlimited access to your AI account.
Gate/AI implements this using a combo of standards and platform features:
- Device attestation (e.g., Apple’s App Attestation, Android’s Play Integrity) to prove the app and device haven’t been obviously tampered with.
- Sender-constrained tokens like DPoP (Demonstration of Proof of Possession) so that even if a token leaks, it’s tied to a specific device key and can’t be replayed from somewhere else.
- Short-lived, scoped tokens that expire quickly and only allow the minimal operations your app needs.
If you want to go deeper into how the zero-trust flow actually works, see:
- “Zero-Trust AI Access from Mobile with DPoP and App Attestation” (how attestation + DPoP fit together).
- “What is DPoP for OAuth?” (how sender-constrained tokens prevent replay).
- “What is Apple’s App Attestation Framework?” (how iOS proves app integrity).
- “Why shipping secrets in your app is a terrible idea” (the threat model you’re trying to avoid).
Those articles walk through the lower-level details; this page is the 10,000-foot view.
Why a mobile AI gateway is better than “just shipping the key”
If you’re a mobile dev, the alternatives usually look like this:
- Ship the AI key in the app. Easiest path. Also the fastest path to leaked keys, surprise bills, and awkward security reviews.
- Roll your own backend. More secure, but now you’re on the hook for auth, rate limiting, logging, scaling, incident response, and keeping up with new AI providers.
- Use a generic API or AI gateway. Good for backend services, but you still have to solve the “how do I safely call this from a mobile app?” problem yourself.
A mobile AI gateway like Gate/AI is a fourth option:
- You get the simplicity of “call one HTTPS endpoint from the app.”
- You avoid running and maintaining your own backend just to broker AI calls.
- You get mobile-aware security: no shipped secrets, device attestation, DPoP, short-lived tokens, per-device policy, usage monitoring, and cost controls.
In practice, this means you can add “Call OpenAI” or “Chat with your data” features to your iOS/Android/React Native/Flutter app without first becoming an OAuth expert or building out a mini security team.
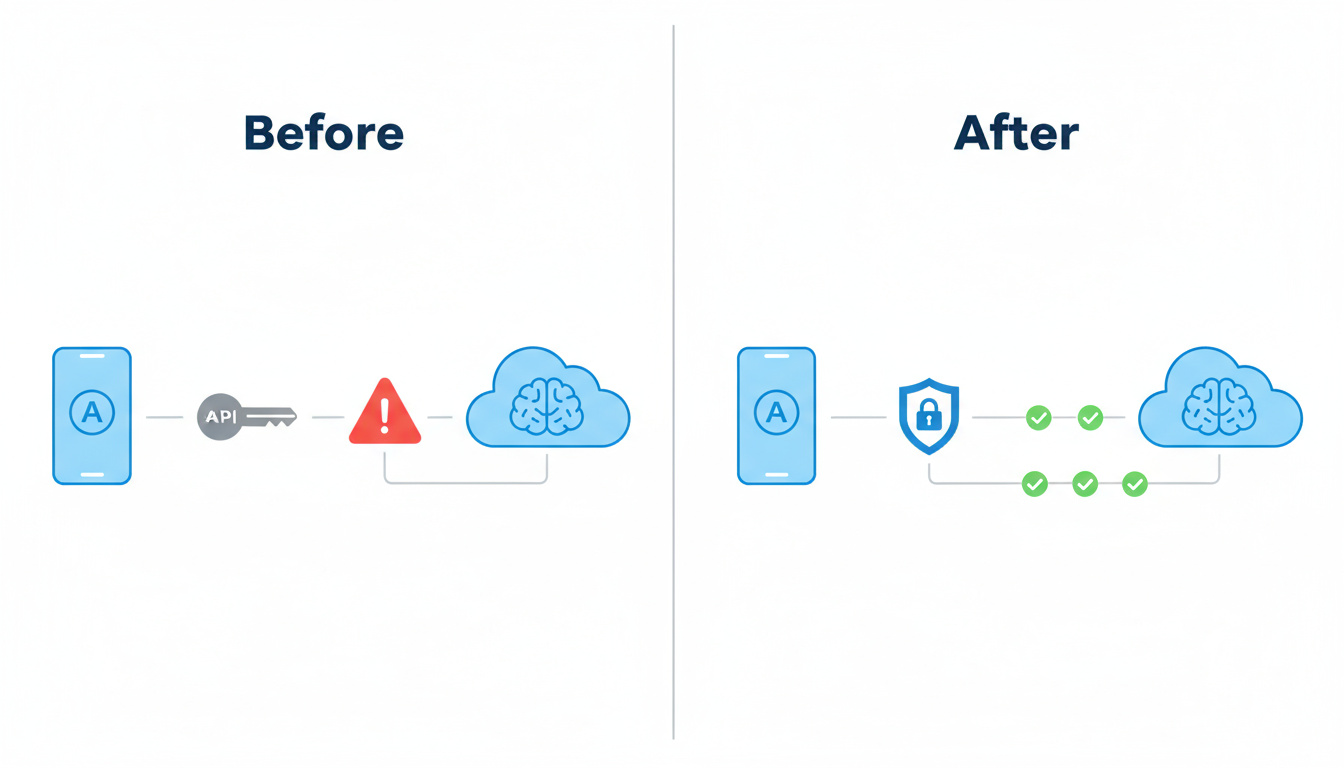
How Gate/AI executes the zero-trust playbook
Zero trust on mobile means every call is verified, scoped, and observable. Gate/AI applies that philosophy without asking you to babysit infrastructure. Attestation proves the app is running on a legitimate device build. Proof-of-possession ensures tokens can’t be replayed from a script. Policy guardrails keep spend and abuse in check even if someone clones the binary. All of that happens before the request leaves your control.
Want to see each building block in action? Dive into the dedicated breakdowns:
- Learn why secrets must stay off-device in Why shipping secrets in your app is a terrible idea.
- See how sender-constrained tokens work in What is DPoP for OAuth? and why that matters for replay resistance.
- Understand how device attestation underpins trust with What is Apple’s App Attestation Framework? and What is Google’s Play Integrity Service?.
Those pieces snap together inside Gate/AI so your client can stay stateless while the gateway enforces zero-trust policy at the edge.